Cheatsheet
Yup validation references that are not easy to find on yup documentation.
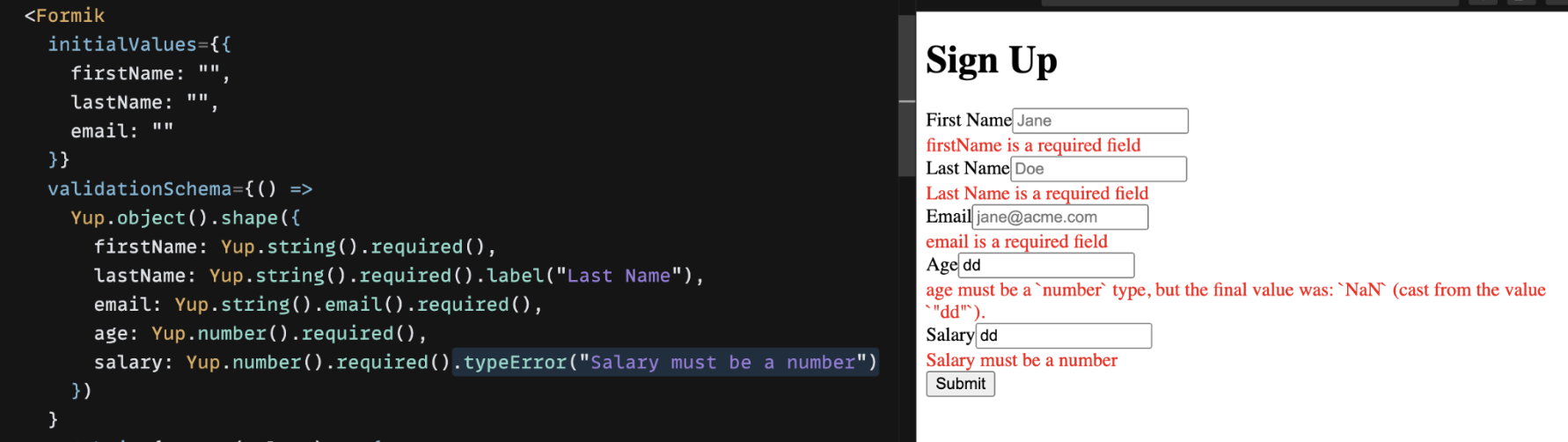
Custom type errors
If type validation fails, give a custom error to display.
Yup.number().typeError("Salary should be a number") })
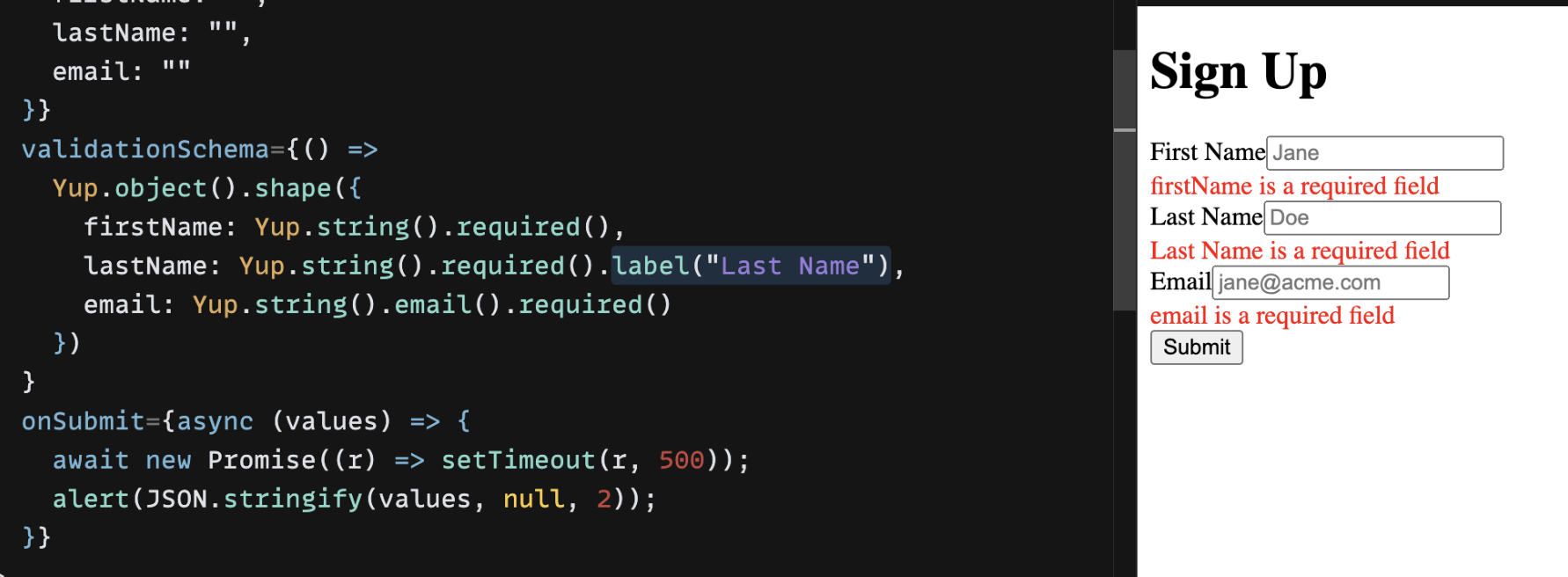
Field label for error
By default formik will show name given for the input element in error message. We can override it by providing custom label for field.
Yup.number().min(0).max(99).required().label("Custom Label")
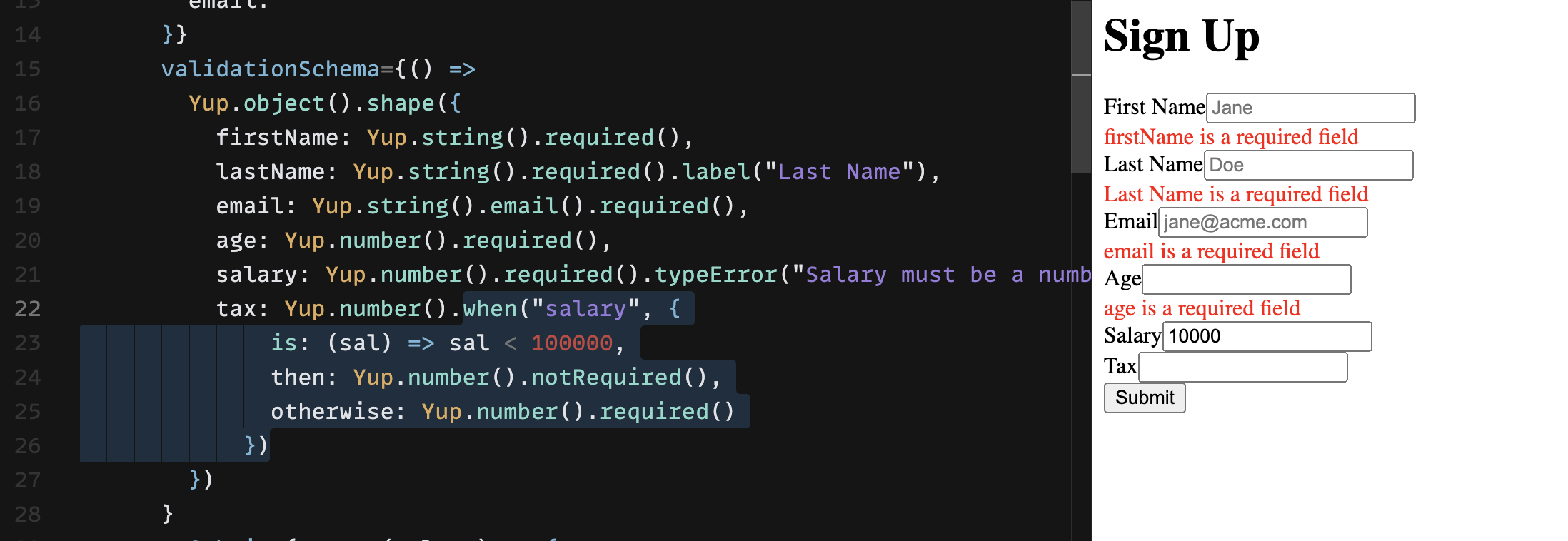
Dependent Validations
Yup can validate fields based on values of other fields. For example if you have to validate Tax field should be required only when Salary > 100000.
Yup.number().when("salary", {
is: (sal) => sal < 100000,
then: Yup.number().notRequired(),
otherwise: Yup.number().required()
})
Note: when() validations works across siblings. You can provide any other field that is sibling (on the same level) as the current field.
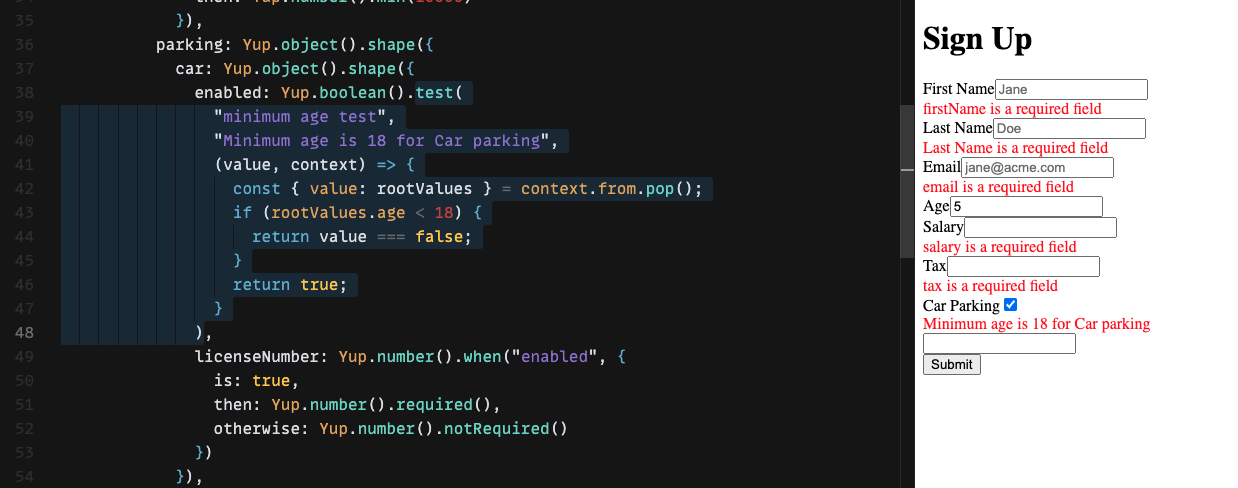
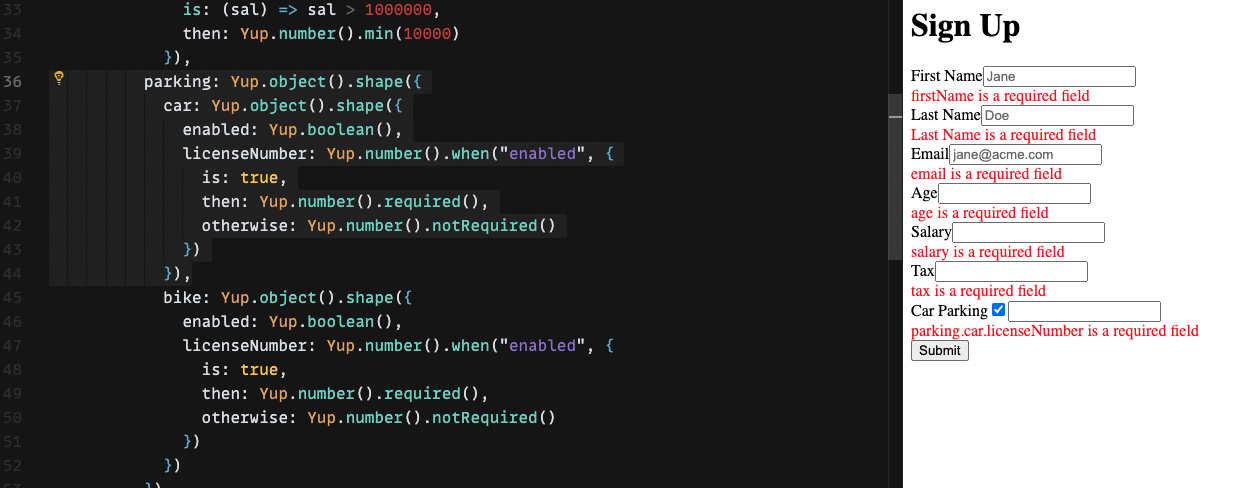
Nested Object Validations
When you need to perform nested validations for a form having structure like parking: { car: { enabled: true, licenseNumber: 1234 }}. The "name" attribute on form fields can be set by destructuring with dots like "parking.car.enabled"
parking: Yup.object().shape({
car: Yup.object().shape({
enabled: Yup.boolean(),
licenseNumber: Yup.number().when("enabled", {
is: true,
then: Yup.number().required(),
otherwise: Yup.number().notRequired()
})
})
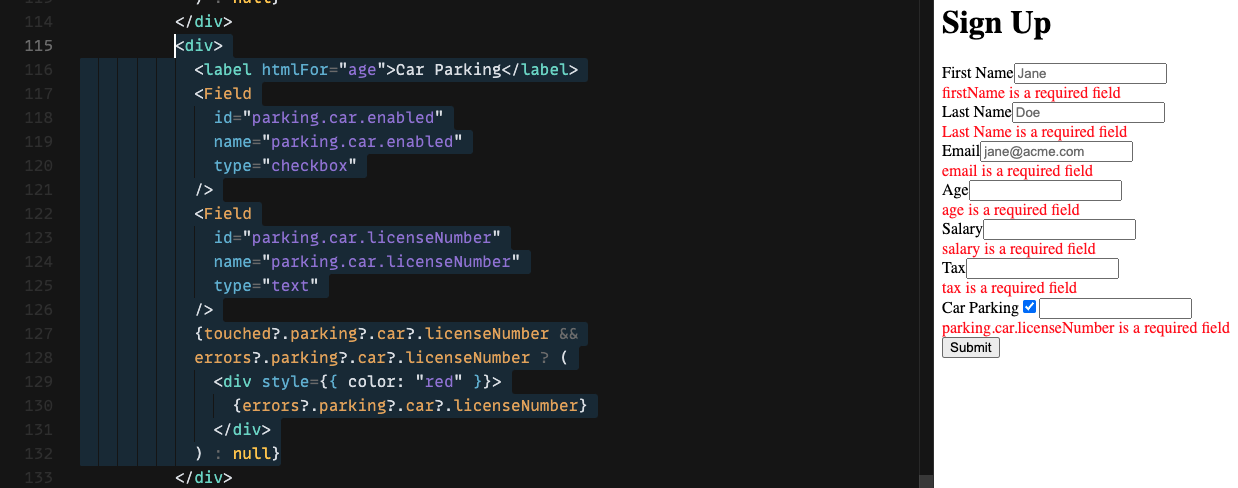
Referring parent level field value in Yup validations
When we have a form structure like below and want to put validation for car.parking.enabled should be unchecked if age is less than 18.
{
firstName: "",
lastName: "",
email: "",
parking: Object,
car: {
enabled: true
},
age: "33",
}
We can not access value for age in when() condition as it is on a parent level. We can use context object passed in test() method by yup.
enabled: Yup.boolean().test(
"minimum age test",
"Minimum age is 18 for Car parking",
(value, context) => {
const { value: rootValues } = context.from.pop();
if (rootValues.age < 18) {
return value === false;
}
return true;
}
),